What is coronary artery disease?
cungkring.com: The causes of coronary heart disease
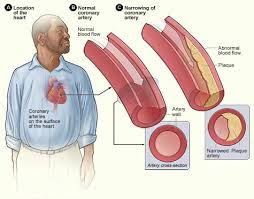
The most common cause of CAD is a vascular lesion with cholesterol plaque buildup in the arteries, called atherosclerosis. Reduced blood flow occurs when one or more of these arteries becomes partially or completely blocked.
The four main coronary arteries are located on the surface of the heart:
right coronary artery
left main coronary artery
left circumflex artery
left anterior descending artery
These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood and nutrients to your heart. Your heart is a muscle that is responsible for pumping blood throughout your body. According to the Cleveland Clinic, a healthy heart moves 3000 gallons of blood through your body every day.
Like any other organ or muscle, your heart must receive sufficient, reliable blood to complete its work. The decreased blood flow to your heart can cause symptoms of CAD.
Other rare causes of damage or obstruct a coronary artery also restrict blood flow to the heart.
Symptoms of CAD
When your heart is not getting enough of arterial blood, you may experience a variety of symptoms. Angina pectoris (chest pain) is the most common symptom of CAD. Some people describe it as discomfort:
chest pain
heaviness
stiffness
burning
pressing
These symptoms can also be mistaken for heartburn or indigestion.
Other symptoms of CAD include:
pain in the arms or shoulders
breathlessness
sweat
dizziness
You may experience more symptoms when your blood flow is more restricted. If a blockage cuts off blood flow completely or almost completely, your heart muscle will begin to die if not restored. This is a heart attack.
Do not neglect any of these symptoms, especially if they are unsustainable or last longer than five minutes. Immediate medical treatment is necessary.
Symptoms of CAD for women
Women may also experience the symptoms above, but they are also more likely to have:
nausea
vomiting
Back ache
jaw pain
shortness of breath without feeling pain in the chest
Men have a higher risk of developing heart disease than premenopausal women. Postmenopausal women by age 70 have the same risk as men.
Due to the decreased blood flow, your heart can also:
become low
develop abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia) or rates
unable to pump as much blood as your body needs
Your doctor detects these cardiac abnormalities during diagnosis.
The CAD risk factors
Understanding CAD risk factors may help with your plan to prevent or reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.
Risk factors include:
hypertension
high blood cholesterol
smoking
resistance to insulin / blood sugar / diabetes mellitus
obesity
inactivity
bad eating habits
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
emotional stress
excessive consumption of alcohol
history of preeclampsia during pregnancy
The risk of CAD also increases with age. only according to age as a risk factor, men have a higher risk for the disease by the age of 45 years and women have a higher risk from the age of 55. The risk of coronary heart disease also higher if you have a family history of the disease.
powered by Rubicon Project
diagnose CAD
Diagnosing CAD requires a review of your medical history, physical examination and other medical tests. These tests include:
ECG: This test checks the electrical signals that travel through your heart. It can help your doctor determine if you have had a heart attack.
Echocardiogram: This wave imaging test used to create an image of your heart. The results of this test indicate that certain things in your heart working properly.
Stress test: This test measures the particular stress on your heart during exercise and at rest. The test monitors the electrical activity of your heart while you walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike. Nuclear imaging can also be performed for part of this test. For those who can not perform physical exercises, some drugs can be used instead for stress tests.
Cardiac catheterization (heart cath left): During this procedure, your doctor injects a special dye into your coronary arteries through a catheter inserted into an artery in the groin or forearm. The dye helps to improve the radiographic image of your coronary arteries to identify blockages.
Heart CT scan: Your doctor may use this imaging test to check for calcium deposits in the arteries.
What is the treatment for CAD?
It is important to reduce or control your risk factors and seek treatment to reduce the risk of heart attack or stroke if you are diagnosed with CAD. Treatment also depends on your current health status, risk factors, and the general welfare. For example, your doctor may prescribe a treatment medications to treat high cholesterol or high blood pressure, or you may receive medication to control blood sugar if you have diabetes.
Changes in lifestyle can also reduce your risk of heart disease and stroke. For example:
quit smoking
reduce or stop your alcohol consumption
regular exercise
Slimming at a healthy level
eat a healthy diet (low fat, low sodium)
If your condition does not improve with lifestyle changes and medications, your doctor may recommend a procedure to increase blood flow to your heart. These procedures can be:
Balloon angioplasty: to widen blocked arteries and smoosh the buildup of plaque, usually performed with the insertion of a stent to help keep the lumen open after the procedure
Bypass graft coronary artery to restore blood flow to the heart open chest surgery
Enhanced external counterpulsation: to stimulate the formation of new small blood vessels naturally bypass clogged arteries in a noninvasive procedure.

0 Komentar
Post a Comment